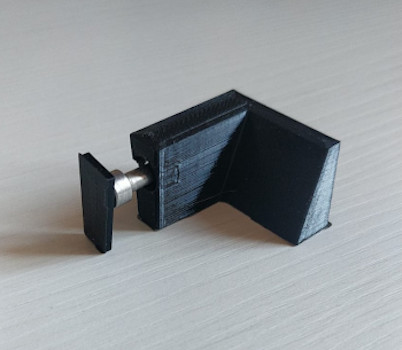
We recently entered the world of 3D printing to find solutions to certain questions that arise during our work.
This represents a great advantage for our company that allows us to produce some useful details for our maintenance and repairs on boats.
One of the main strengths in this area is the possibility of having at your disposal, during the design phase, the maximum customization on sizes, shapes and materials.
We have managed to develop an efficient 3D printing process with the support of professionals who assure extreme precision and accuracy in both projects and finished prints. By collaborating, we are able to focus on every detail so that the final result is suitable for the needs of the specific boat, while remaining a quality product, resistant and functional.
How does a 3D printer work?
The basic operation of a 3D printer is quite similar to the one of a normal printer: you create a project on a special software from your computer to be sent to the printer, complete with all the details of the final product (length, depth, materials to be used, etc.), and the machine prints it. Generally, the format used to save a project for printing is the Stl (Standard Triangulation Language To Layer), a format that breaks down the project into graphic triangles so that it is easy for the printer to reproduce the initial drawing.
After starting printing, in a short time, you will have in your hands what just a short time was just a project on a screen. The main difference between these two types of printers lies in the fact that in a 3D printer the extruder, instead of ink, uses the polymers of the chosen materials. The filaments in the form of granules are heated, melted and stratified at high temperatures until the construction process is completed.
What materials can be used?
Based on the new discoveries and innovations that technology brings, the materials that can be used in 3D printing also change every year.
In fact, today there is a wide variety of usable materials, available in different forms (powder, filaments, pallets, granules, resins, etc.), which change depending on how you use them.
The materials can be:
– plastics such as PLA, PETG, PEC, Filoalfa, N-ASA, ABS, alumide, etc;
– metallic composites which can be derived from aluminum, cobalt, steel, titanium, gold, silver, etc;
– in ceramic (ceramic resin);
– paper;
– biological materials for food or textile printing.
There are also some special materials which are less common.
These are composite materials such as WOOD PLA which contains wood fibers and produces a very particular woody finish. Very smooth, freshly printed the material produces a pleasant smell of real wood. Another rare material can be GLASS PLA, translucent and very resistant, with a not completely transparent finish due to the parts of PLA.
Some others are CARBON FIBER and FLEXY.
The 3D printer in the nautical sector
It is interesting to see in which specific areas these new machines are used; these can be used in various sectors, from food production to the medical field, with the printing of prostheses and organic fabrics.
Regarding our sector, the nautical one, 3D printers can prove to be very useful and in fact there are many who today, in the world of navigation, rely on 3D printers. We witnessed these innovations at the Genoa Boat Show of 2020.
There it was surprising the idea of Moi Composites, section of the Politecnico di Milano, of directly printing a motor boat with Continuous Fiber Manufacturing (CFM) 3D printing technology.
The project for the boat, called MAMBO (Motor Additive Manufacturing BOat), was inspired by Sonny Levi’s Arcidiavolo. MAMBO is 6.5 meters long, has a maximum beam of 2.5 meters, weighs 800 kg and is equipped with a 115 hp outboard engine, a navigation system, cork deck and white leather sofas.
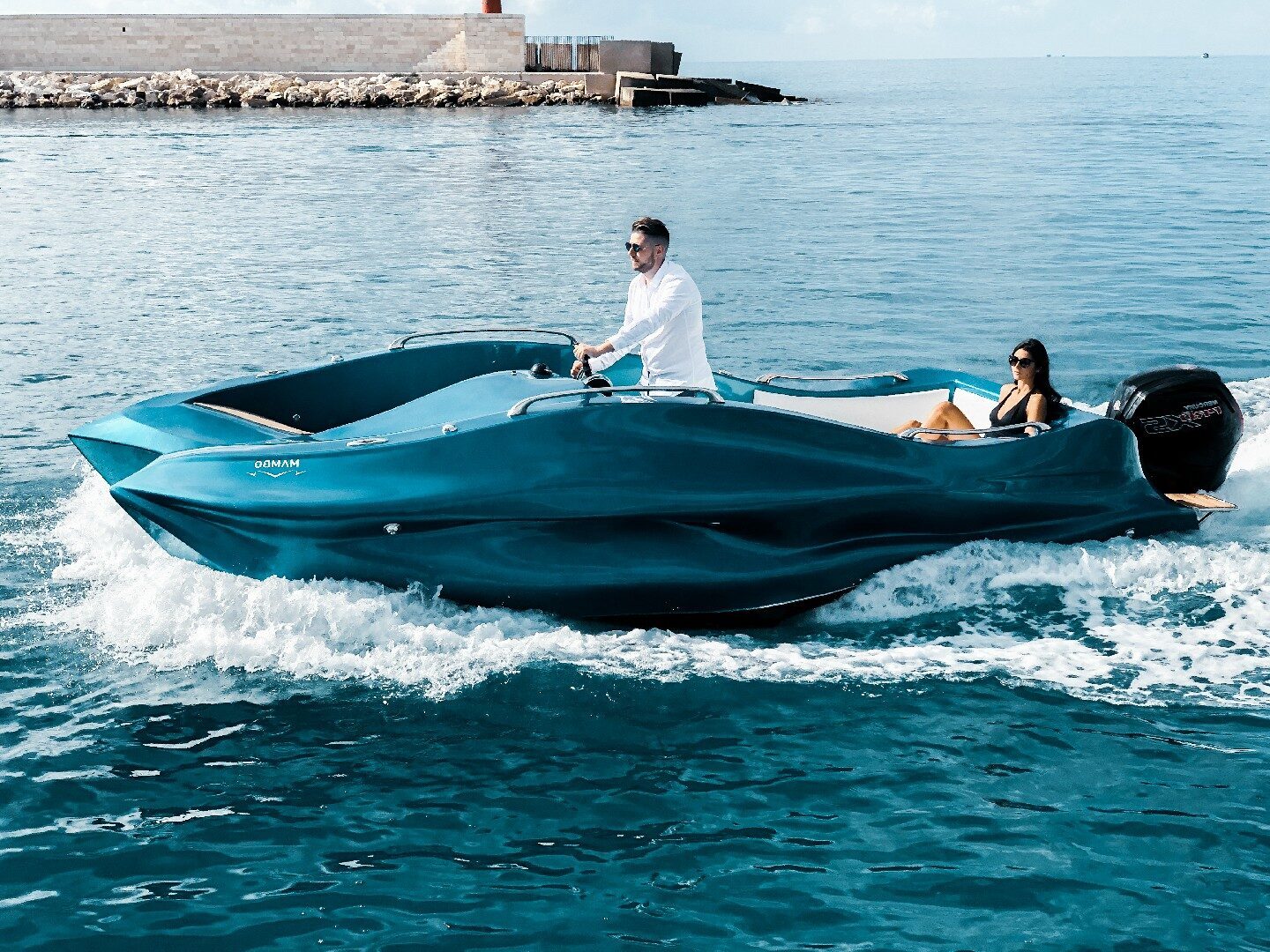

The construction of MAMBO did not require, as usually happens, the construction of a model and therefore of a mold in which laminate the boat. This has made it possible to create a hull that has concave and convex shapes which, in traditional production, would require the creation of different molds and relative hull sections that would need to be jointed together to obtain the complete product.
Advantages in using a 3D printer
Having a 3D printer offers several advantages, such as:
– reduction of warehouse costs: by producing the spare parts by oneself directly on site, when possible, you can cut on storage and shipping costs;
– time reduction: time is saved both on production and on the on-site availability of the material needed to build the part, without waiting for shipment from the manufacturer’s central warehouse;
– customization of products: by choosing the shapes, sizes and materials of the pieces by yourself, you will have prints perfectly suitable for the specific boat;
– greater energy efficiency: less waste and less fuel consumption.
With our specialized team, here at Seven Seas, we started producing some necessary parts for our works and we clearly saw the real advantage of having a 3D printer at our disposal.
After accurate measurements and designs, we are able to print small details without having to rely on other suppliers, saving on time and costs, without ever giving up on quality and functionality.